Trust registration in india establishes a legal entity for social welfare, education, or private asset management. This guide explores how to register a trust in india using the trust registration process. We cover the trust registration fees, the documents for trust registration, and charitable trust registration online. Understanding trust registration ensures legal standing, tax benefits, and public credibility. Our expertise helps you navigate trust deed registration for long-term organizational success.

Understanding the Fundamental Trust Registration Process
The trust registration process is a systematic legal journey that defines your organization’s future. It begins with the settlor expressing a clear intention to create a trust entity. You must choose a unique name that reflects your organizational mission. This name must not infringe upon existing trademarks or violate restricted legal words. The settlor then transfers property to trustees for the benefit of specific individuals.
Appointing the right trustees is a vital part of how to register a trust. For charitable purposes, you generally need a minimum of three competent trustees. Private trusts usually require at least two trustees to manage the property effectively. Trustees must be individuals who are not disqualified by law from holding property. They are legally bound to manage the assets according to the trust’s stated goals.
The next stage of the trust registration process involves choosing a physical registered office. You must provide proof of ownership or a valid rent agreement for this office. If the office is on rented property, a No Objection Certificate is mandatory. All trustees must agree on the trust’s specific objectives before drafting the deed. Clearly defined goals ensure the trust remains compliant with Indian law over time.
Drafting for Trust Deed Registration
The core of your legal entity is the trust deed registration document. This formal legal document outlines the governance and charitable purpose of the trust. It specifies the names and addresses of the settlor, trustees, and beneficiaries. The deed must describe the trust property or corpus being transferred. It also details the powers, rights, and obligations of every appointed trustee.
A well-drafted deed includes a procedure for the amendment or removal of trustees. It must also contain a clear termination or dissolution clause for the organization. You must execute this document on non-judicial stamp paper of appropriate value. The settlor and all trustees must sign every page of the deed. At least two independent witnesses must also sign to attest the signatures.
Successful trust deed registration makes the document part of the official public record. This status provides legal enforceability and prevents future disputes among family or members. Registration is mandatory if the trust holds immovable property like land. Even with movable property, registration is strongly advised for accountability and standing. The registered deed acts as vital evidence in legal or administrative proceedings.

Mandatory Documents Required for Trust Registration
Gathering the correct documents required for trust registration ensures a smooth application. You must provide identity proof for the settlor, trustees, and witnesses. Aadhaar cards, PAN cards, or valid passports are acceptable forms of identification. Recent passport-size photographs of all key parties are also a strict requirement. These documents verify the identity of the individuals managing the trust assets.
| Document Category | Specific Items Needed | Legal Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Core Entity Proof | Original Trust Deed on Stamp Paper | Defines governance and legal purpose |
| Identity Verification | PAN and Aadhaar of all Trustees | Verifies the identity of managing members |
| Address Verification | Rent Agreement or Sale Deed | Confirms the trust's physical location |
| Ownership Consent | No Objection Certificate (NOC) | Grants legal right to use the premises |
| Financial Record | PAN Card of the Organization | Required for bank and tax compliance |
You must also submit documents for trust registration related to the office premises. This includes a utility bill or a bank statement for the office address. If the property is owned, you must provide the registered sale deed. For rented spaces, a registered lease deed or rent agreement is necessary. All documents for trust registration must be clearly scanned and ready for submission.
Breakdown of Trust Registration Fees and Costs
The trust registration fees vary significantly across different states in India. Stamp duty represents the largest portion of the total registration cost. In Delhi, the duty is roughly 8% of the property’s total value. Maharashtra often charges a lower rate of approximately 2% for trust property. You should verify the current local rates before purchasing stamp paper.
There are also specialized trust registration fees for specific government organizations. The National Trust charges fees based on the location of your NGO. Organizations in urban areas must pay a fee of Rs. 2000. NGOs located in rural areas are charged a reduced fee of Rs. 1000. These fees are typically deposited electronically during the trust registration online process.
Legal consultation and drafting services also contribute to the overall expenditure. Professional expertise ensures that your trust deed is legally sound and compliant. It prevents future delays caused by document errors or procedural confusion. You should budget for these professional costs alongside the statutory registration fees. Accurate budgeting helps founders launch their organizations without unexpected financial hurdles.
Specialized Charitable Trust Registration Online
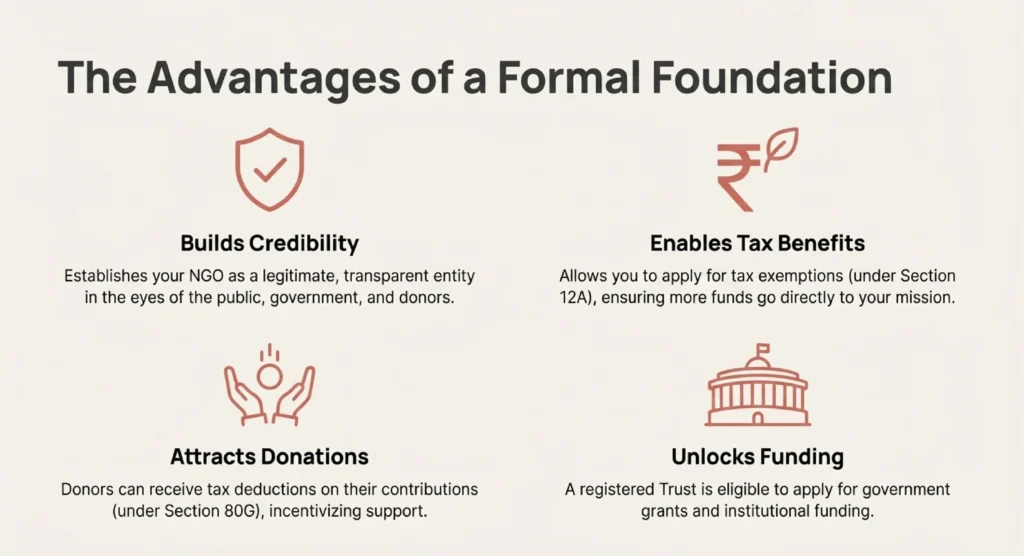
Charitable trust registration online is the primary gateway to tax exemptions. NGOs must register under Sections 12A and 80G of the Income Tax Act. Section 12A provides the conditions for total tax exemption on trust income. Section 80G allows donors to claim deductions on their contributions to the trust. This incentive is vital for attracting individual and corporate donations.
The charitable trust registration online process involves using specific digital forms. You must use Form 10A for initial or provisional tax registration. Form 10AB is used to convert provisional status into permanent registration. These applications are submitted through the official Income Tax India portal. Recent updates require detailed disclosures of the trust’s assets and liabilities.
You must also disclose any income derived from religious activities. Transparency is now a core requirement for maintaining your tax-exempt status. The authorities may also ask for your NGO-Darpan Portal registration details. This integration ensures that the government can track all active charitable entities. Regular compliance with these digital filings prevents the loss of tax benefits.

Exploring Trust Registration Online for Disabilities
Specialized NGOs must navigate trust registration online for disability welfare schemes. The National Trust supports NGOs working with Autism and Cerebral Palsy. It also covers individuals with Intellectual Disabilities or Multiple Disabilities. To be eligible, your NGO must already be a registered trust or society. You must also be listed on the NGO Darpan Portal.
The online application requires you to fill out detailed organizational information. You must upload all documents for trust registration in PDF format. An E-form is automatically generated by the system for the head to sign. This signed and stamped form must be scanned and re-uploaded. Ensure each uploaded file remains under the 5MB size limit.
Registration with the National Trust allows access to specialized government benefits. It builds immense trust among beneficiaries and the local community. If your application is rejected, you must wait six months to reapply. Providing false information during the trust registration online process leads to blacklisting. Accurate reporting and documentation are the only ways to ensure approval.
Technical Details on How to Register a Trust for Education
Educational trusts are non-profit entities dedicated to advancing academic standards. When learning how to register a trust in india for education, focus on the mission. These trusts offer scholarships, assist facilities, and improve the quality of learning. Founders must ensure the trust operates without any individualized profit motives. Any surplus funds must be reinvested solely into educational pursuits.
Educational work can also be performed by an Educational Society. Societies are often preferred for opening formal schools or colleges. Registration as a society helps in obtaining government land and grants. You must choose between the Indian Trusts Act and the Societies Registration Act. Both structures require a defined governance system of board members.
The trust registration process for education can take several months. This timeline accounts for the scrutiny of proposed educational activities. Authorities may regularly check your conformity with prescribed academic standards. This includes curriculum guidelines, teacher qualifications, and infrastructure requirements. Maintaining high standards ensures your educational trust remains credible and effective.
How to Register a Trust in India for Private Families
A private trust is a crucial tool for managing family wealth. When considering how to register a trust in india for families, transparency is key. This structure offers a legally shielded method for asset distribution. It helps in avoiding rising conflicts among family members over property. Private trusts are created to benefit identified individuals rather than the public.
You must identify the four key elements: settlor, trustee, beneficiary, and property. The settlor establishes the trust and transfers the family assets. The trustee holds and manages these assets for the family’s benefit. Beneficiaries are the recipients who receive the trust’s financial assistance. Clear definitions of these roles reduce the likelihood of future legal disputes.
| Private Trust Type | Level of Settlor Control | Trustee Flexibility | Primary Tax Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revocable Trust | High (Can withdraw) | Low (Fixed shares) | Taxed at Settlor’s rate |
| Irrevocable Non-Discretionary | Low (No withdrawal) | Low (Fixed shares) | Taxed at Beneficiary’s rate |
| Irrevocable Discretionary | Low (No withdrawal) | High (Flexible shares) | Taxed at Maximum Marginal Rate |
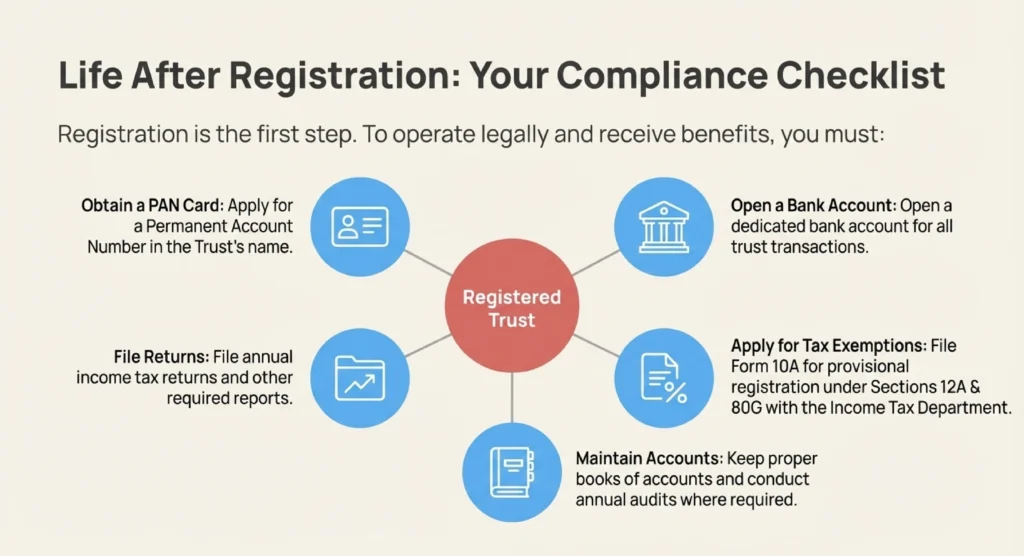
The Irrevocable Discretionary Trust is often preferred for family wealth. It allows the trustee to adjust distributions based on changing financial needs. This flexibility is vital for long-term succession and financial planning. You must apply for a PAN and open a bank account post-registration. This ensures that all family financial transactions remain compliant and transparent.
Final Checklist for Documents for Trust Registration
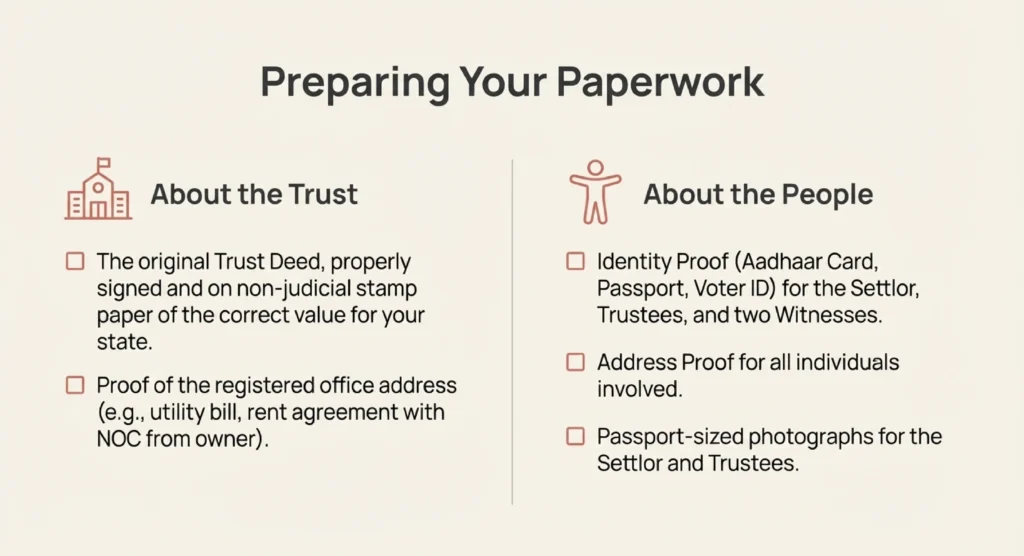
Reviewing your documents required for trust registration prevents procedural delays. You must have the original signed trust deed ready for the registrar. Ensure all identification papers are up to date and verified. If any document is not in English or Hindi, provide a translation. This translated version must be attested by the head of the organization.
Successful trust registration requires regular audits of your financial accounts. You must maintain transparent books of accounts for annual scrutiny. Audited statements must be accessible to both stakeholders and government authorities. Filing annual tax returns using Form ITR-7 is a mandatory requirement. These steps protect your trust’s legal standing and tax-exempt status.
If you work with specific disabilities, check the National Trust guidelines. They provide specific electronic forms that must be signed and stamped. Registration provides your NGO with the foundation for lasting social impact. Following these structured steps ensures your trust is built on legal credibility. Always consult with professionals to handle complex state-specific registration requirements.
Maintaining Ongoing Legal Compliance
Registration is the first step toward a long-term charitable mission. Trusts must adhere to labor laws and anti-discrimination policies. Infractions can result in penalties or the suspension of registration. You should hold regular trustee meetings as specified in your deed. These meetings ensure that the management remains aligned with the trust’s objectives.
Public trusts must reinvest all income into their welfare activities. Private trusts must manage tax liabilities if non-relatives are included. Ambiguity in beneficiary definitions can lead to significant tax issues. Seeking expert advice helps you navigate these complex legal nuances. Your commitment to compliance will foster donor trust and organizational growth. By following this guide, you can successfully establish a trust in India.
Frequently Asked Questions for NGO Compliance
Registration is mandatory if the trust holds any immovable property like land. Even for movable property, registration is strongly advisable for legal standing. It establishes your organization as a credible entity for receiving public donations.
You need the original trust deed, identity proofs, and photographs of all trustees. Proof of the registered office address and an owner’s consent letter are essential. Verified copies of registration and income tax certificates are also required.
First, select a unique name and draft a legally binding trust deed. Then, appoint at least three trustees and submit documents to the local registrar. Finally, obtain the certificate and apply for a permanent account number.
The formal registration of a deed usually requires a physical visit for signatures. However, specialized National Trust applications and tax benefit filings are handled through online portals. Most jurisdictional portals allow for the electronic submission of scanned PDF documents.
Fees depend on state-specific stamp duty and the total value of trust property. National Trust registration costs Rs. 2000 for urban and Rs. 1000 for rural areas. Professional legal drafting and compliance assistance may involve additional varying costs.
You must apply via the official Income Tax Portal using Forms 10A or 10AB. This process provides necessary exemptions under Sections 12A and 80G for charitable activities. Accurate disclosure of all assets, liabilities, and religious income is now strictly mandatory.
The timeline typically ranges from two to four weeks for most standard trust types. Educational trust procedures might extend to several months due to additional document scrutiny. Starting the procedure early allows enough time for follow-up queries from authorities.
Educational trusts must operate strictly for non-profit purposes and academic advancement. All surplus funds must be reinvested into the trust’s stated educational goals. Founders must ensure no individualized gain or profit distribution occurs among the trustees.
Registration makes the deed a public record and ensures its legal enforceability. It clearly defines the governance structure and protects the trust from future disputes. A registered deed is a prerequisite for opening a bank account.
The trust deed can be amended if the original document includes a specific clause. Any major amendments must follow fresh registration formalities depending on specific state laws. You must inform the registrar and update your records to maintain compliance.
