FCRA Registration Procedure – Step-by-Step Guide for NGOs
In an increasingly interconnected world, non-profit organizations, charitable trusts, and Section 8 companies in India often receive crucial financial support from international donors. This foreign contribution plays a vital role in funding various cultural, economic, educational, religious, and social development projects across the nation. To ensure these funds are utilized responsibly and in alignment with national interests, the Indian government has established a robust regulatory framework known as the Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010 (FCRA).
Compliance with FCRA is not merely a legal formality; it is a fundamental requirement for any entity wishing to accept and manage foreign donations. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the intricacies of FCRA registration and, more critically, its renewal process, offering a clear roadmap for organizations to maintain their eligibility for international funding.

Understanding the Essence of FCRA
The Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010, is a pivotal legislation designed to regulate the acceptance and utilization of foreign contributions and foreign hospitality by individuals, associations, or companies in India. Its primary objective is to create a transparent framework that prevents any potential misuse of foreign funds that could be detrimental to the country’s interests. The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) is the governing authority responsible for overseeing and monitoring FCRA compliance, including the registration of non-profit organizations.
Why FCRA Registration is Essential:
For any organization dedicated to social upliftment or humanitarian causes, securing FCRA registration is paramount. Without it, accepting foreign donations is legally prohibited and can lead to severe penalties. The benefits of obtaining this registration are multifaceted:
- Access to Foreign Funding: It removes legal barriers, enabling associations to accept foreign donations for various projects.
- Transparency and Accountability: The framework promotes transparency in how foreign contributions are received and utilized by NGOs and social trusts.
- Legal Protection and Support: Registered organizations gain significant government support, including potential tax exemptions, ensuring their operations are legally sound.
- Preventing Financial Misuse: The government leverages FCRA to prevent the misuse of foreign funds, thereby understanding the true nature of donations and their application towards organizational goals.
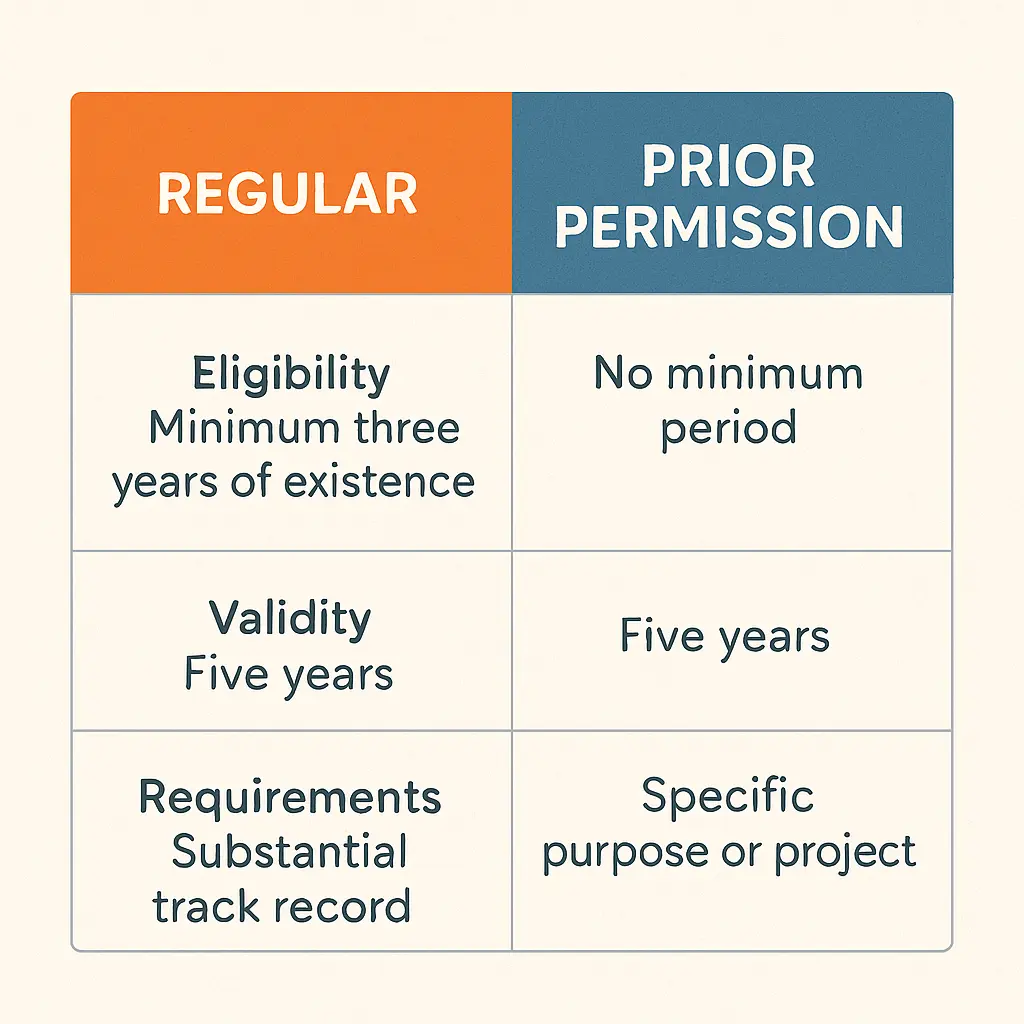
Types of FCRA Registration and Eligibility Criteria
The FCRA framework offers two primary routes for registration: Normal Registration and Prior Permission (PP) registration, each catering to different organizational stages and needs.
1. Normal Registration: This category is typically for organizations that have a proven track record of social service. To qualify for normal registration, an applicant must meet several key requirements:
- Legal Standing: The applicant must be formally registered under relevant Indian laws, such as the Companies Act, 2013 (as a Section 8 company), the Societies Registration Act, 1860, or the Indian Trusts Act, 1882.
- Track Record: The organization must have actively undertaken activities in its chosen social field and demonstrated substantial contributions.
- Financial Commitment: A minimum expenditure of INR 1 Crore (excluding administrative costs) towards its objectives must have been allocated over the preceding three years.
- Audited Financials: Submission of audited financial statements for the past three years, duly verified by certified chartered accountants, is a mandatory requisite.
- Specific Donor Commitment: The organization must provide a detailed commitment letter from a foreign donor, specifying the amount of payment and the intended purpose.
- Relationship Between Organizations: Strict guidelines apply if there is an overlap in members or office bearers between the foreign donor organization and the Indian receiving organization. For instance, the Chief Functionary of the Indian organization cannot be part of the donor organization, and foreign members/employees cannot constitute more than 51% of the governing body or office bearers of the Indian entity. Similar rules apply in the case of individual foreign contributors to prevent potential conflicts of interest.
Essential Documentation for FCRA Registration
A robust application for FCRA registration hinges on the submission of accurate and complete documentation. Key documents generally include:
- Self-attested copies of the organization’s foundational documents, such as the trust deed, formation certificate, or Memorandum and Articles of Association (MOA and AOA).
- Information pertaining to the non-profit organization, including its Permanent Account Number (PAN).
- A clear impression of the Chief Authority, typically in JPG format.
- A comprehensive activity report detailing the organization’s work over the previous three years.
- Audited financial statements for the last three years, which must include the Profit & Loss account, income and expenditure details, and the cash flow statement.
- Certified copies of resolutions adopted by the non-profit body corporate, if applicable, pertaining to foreign contribution.
- A certificate issued in accordance with Section 12 AB of the Income Tax Act.
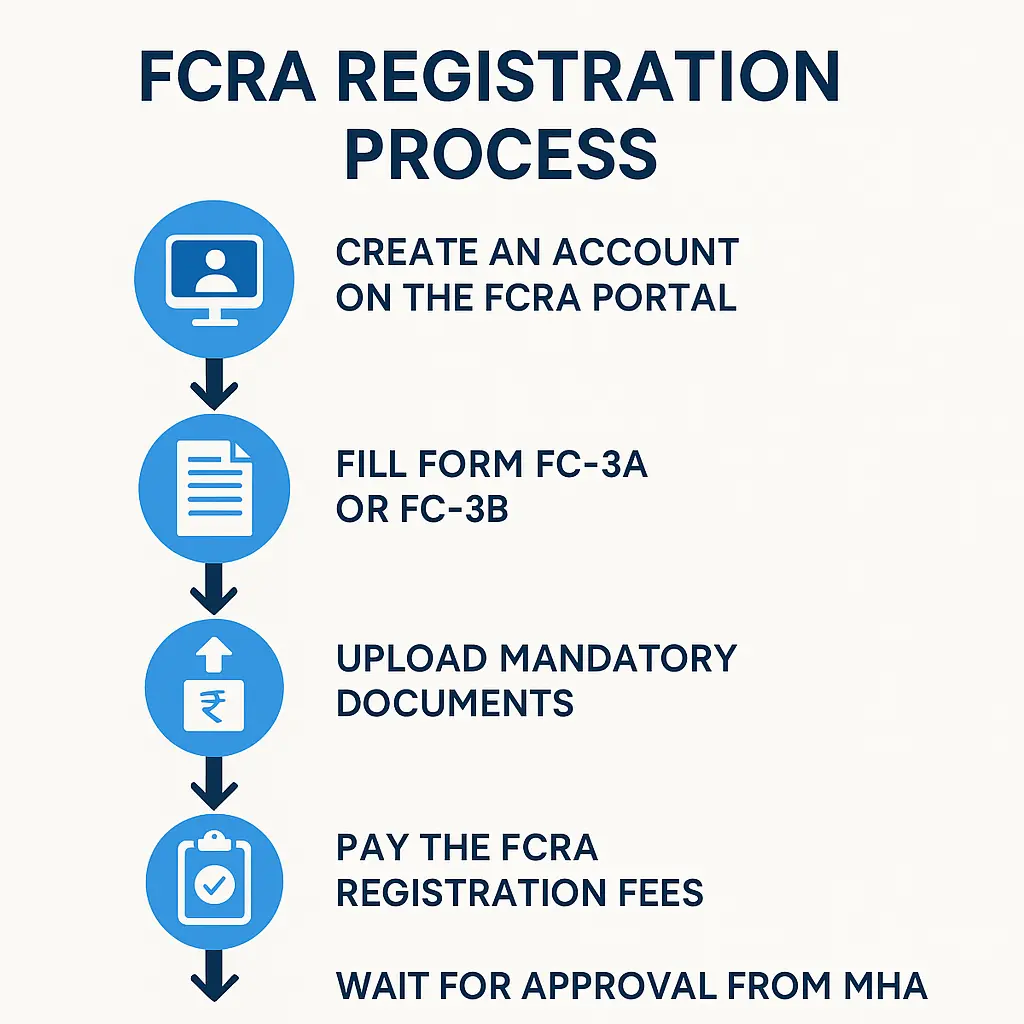
The FCRA Registration Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
The journey to FCRA registration, while detailed, is structured and primarily conducted online. Organizations can typically follow these steps:
1. Access the Official FCRA Website: The initial step involves visiting the Ministry of Home Affairs’ official FCRA web portal.
2. Generate Login Credentials: Applicants need to create a unique login ID and password to access the online system and initiate the registration process.
3. Complete the FC-3 Form: This is the core application form for FCRA registration, requiring precise and comprehensive details about the organization and its proposed activities.
4. Upload Required Documents: All necessary supporting documents must be uploaded in the specified formats and sizes as stipulated on the MHA portal. Errors in format or size can lead to application cancellation.
5. Submit Payment: The final step in the online registration process involves paying the requisite government fees. The fee structure may vary based on the type of FCRA registration being sought.
Upon successful completion and verification, the organization will be registered under FCRA, enabling it to legitimately receive foreign donations.
FCRA Registration Fees: A Clear Breakdown
Understanding the financial commitment involved in FCRA registration is important for budgeting and planning. The government has established a standard fee for this process.
The registration fee for FCRA is INR 10,000. This amount is a mandatory government challan payment required at the time of submitting the initial application for registration under the Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act. This fee facilitates the processing and review of the application by the Ministry of Home Affairs. This payment is typically made online through the FCRA portal during the final stage of the application submission.
FCRA Annual Compliance: Reporting Foreign Contributions
Obtaining FCRA registration is the first step; maintaining compliance is continuous. Organizations that receive foreign contributions are mandated to file annual returns to the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Mandatory Filing: If an NGO or trust’s total income from foreign sources in a financial year exceeds INR 1 crore, filing an FCRA return becomes mandatory.
- Fiscal Year and Deadline: The financial year for FCRA purposes runs from April 1 to March 31. The annual return must be filed by December 31 of the subsequent year, or within nine months after the end of the financial year.
- Form and Content: The return is filed using Form FC-4. It requires a detailed statement of receipts and payments, along with a certified balance sheet, both prepared by a chartered accountant.
- Online Submission: Annual returns, along with the requisite fees, can be conveniently filed through the FCRA online portal, which is designed for ease of use and navigation.
FCRA Renewal: Ensuring Continued Eligibility
FCRA registration is not a one-time process; it is granted for a specific period, typically five years. Therefore, timely renewal is critical for organizations to ensure uninterrupted access to foreign funding.
- The Importance of Timely Renewal: An FCRA certificate is valid for a limited period of five years. To maintain eligibility and avoid a lapse in authorization, it is imperative to initiate the renewal process well in advance of the expiry date. This ensures that the organization can continue to receive and utilize foreign contributions without legal impediments.
- Consequences of Lapsed Registration: Failure to renew the FCRA certificate or submit the application with the correct fees before its expiry can lead to severe consequences. If the certificate ceases to exist, the organization is legally barred from receiving fresh foreign contributions. Furthermore, it cannot utilize any foreign contributions already in hand until the certificate is renewed or a new registration is granted. Any unutilized foreign contributions and assets created from them may vest with the prescribed authority until the situation is rectified.
- Renewal Application Timeline: Organizations are required to file their renewal application at least six months before the expiry date of their existing registration certificate. However, the FCRA portal generally allows applications for renewal to be filed up to one year before the certificate’s expiry date. For example, if a certificate expires on October 31, 2023, the application window for renewal would open on November 1, 2022, and close on April 30, 2023.
- The Renewal Inquiry Process: Recent amendments to the FCRA Act empower the Central Government to conduct thorough inquiries before granting renewal. This process is similar to the verification undertaken during initial registration, ensuring that organizations continue to comply with all provisions of the Act. This means the government can scrutinize an organization’s activities, financial records, and governance structure to ensure continued adherence to national interests.
Step-by-Step Renewal Procedure
The process for renewing FCRA registration is also primarily online:
- Access the Ministry of Home Affairs Website: Navigate to the official FCRA online portal.
- Login to Account: Use the existing login ID and password to access the organization’s profile.
- Fill Electronic Form FC-3C: This specific form is designated for applications for FCRA registration renewal.
- Upload Required Documents: All necessary documents for renewal, as specified, must be uploaded in the correct format and size.
- Pay Renewal Fees: The required government fees must be paid online, and the application form should be printed for records.
Navigating Delayed Renewal Applications

While timely submission is strongly advised, the department may, in certain circumstances, condone delays if satisfactory reasons are provided for not submitting the renewal application by the due date. A delayed application for renewal can typically be filed up to one year from the date of the FCRA Certificate’s expiry.
Delayed Application Fees
If an application for renewal is delayed, or not accompanied by the requisite fee initially, the validity of the certificate is deemed to have ceased. A delayed renewal application will incur a higher fee.
Essential Documents for FCRA Renewal
For the renewal process, organizations must prepare a specific set of documents:
- Self-certified registration certificate of the association.
- Self-certified Memorandum of Association (MOA) or Trust Deed.
- The original FCRA Registration Certificate issued by the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Affidavit of each key functionary within the organization.
- Chief Functionary’s signature (specific pixel dimensions required).
- Seal of the Association (specific pixel dimensions required).
Additionally, organizations should have readily available:
- Detailed information for each key functionary, including Aadhaar for Indian members and a copy of the passport or Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) card for foreign members.
- Details of the designated FCRA bank account at the State Bank of India, Sansad Marg, New Delhi.
- The organization’s Darpan ID, which is mandatory for filing Form FC-3C.
FCRA Renewal Fees
The fee for FCRA renewal is set by the government. The fee for renewing FCRA registration is INR 5,000. This amount is the standard government challan payable when submitting the electronic Form FC-3C for renewal, provided the application is filed within the stipulated timeline. For delayed applications, a higher fee may apply, typically INR 10,000. These fees cover the administrative costs associated with reviewing and processing the renewal application by the Ministry of Home Affairs.
How NGO Partner Supports Your FCRA Renewal
FCRA registration and its subsequent renewal are cornerstones of compliance for any organization in India seeking to leverage foreign contributions for social good. From understanding the types of registration and eligibility to meticulously preparing documents and adhering to filing timelines, each step demands careful attention. While the process can appear complex, adhering to the outlined procedures and requirements is crucial for ensuring legal compliance and sustaining the invaluable work supported by international donors. For organizations seeking expert guidance through these intricate processes, partnering with a knowledgeable entity, such as our company NGO Partner, can simplify compliance, ensuring accurate and timely submission, and ultimately, safeguarding the organization’s mission.
Related Services
- 12A & 80G Registration – Tax exemptions for your NGO and donors.
- NGO Darpan Registration – Get your Unique ID from NITI Aayog.
Frequently Asked Questions
Individuals, associations, companies, NGOs, trusts, and Section 8 companies accepting foreign contributions must register.
Yes, obtaining FCRA registration is mandatory to receive foreign donations in India, as per Section 11 of the FCRA, 2010
Benefits include tax exemptions, attracting foreign donations, legal protection, and preventing financial abuse
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) grants FCRA registration to non-profit organizations and manages the FCRA Department
FCRA registration is valid for a period of five years. Renewal is required before its expiration
The renewal application should be filed six months before the registration certificate expires, using Form FC-3C or FC-3
The government challan for FCRA renewal is Rs. 10,000, payable online during the application process
If the certificate ceases, the organization cannot receive or utilize foreign contributions; unutilized funds may vest with authorities.
Yes, if foreign income exceeds Rs. 1 crore, an annual return in Form FC-4 is mandatory by December 31
Get Started Today
If your NGO is ready to work with foreign donors, don’t delay the registration process. The sooner you begin, the sooner you can secure international support for your projects.
📞 Call NGO Partner now or fill out our contact form to speak with an expert who will guide you through every step of the FCRA registration procedure.
